
Scientific Name
Rachycentron canadum
Common Names
Ling
Lemonfish
Stock Status
Overfishing – Yes
Overfished – No
Recreational Regulations
Federal Regulations
-
Open year-round
- 1 Bag Limit
- 2 Vessel Limit
- Minimum Size: 36 in Fork Length
Notes:
The 2-day bag limit allowance for charter vessels and headboats does not apply to cobia.
For more information, see GulfCouncil.org
The sale of recreationally harvested cobia is prohibited by existing state law in each Gulf state.
To see commercial regulations, download Fish Rules Commercial App for iOS devices or Android devices.
Commercial Regulations
Harvest Limits
| Gulf Zone ACL – 1,738,000 pounds |
| Gulf Zone ACT – 1,564,920 pounds |
These values are expressed in MRIP-FES data currency
Additional Information
Description
Cobia are the only member of their genus. Cobia are long and slim with a broad, flat head. The dorsal side of the fish is dark brown in color, while the ventral side is milky white. The lateral line is dark and obvious, and runs through the eye to the forked tail. Cobia have many small teeth in their mouths, and approximately eight short, unconnected spines between the head and dorsal fin. According to stock characteristics the maximum age is 11 years, the maximum weight is 68 kg (150 pounds) whole weight, and the maximum length is 198 cm (78 inches) total length.
Life History and Distribution
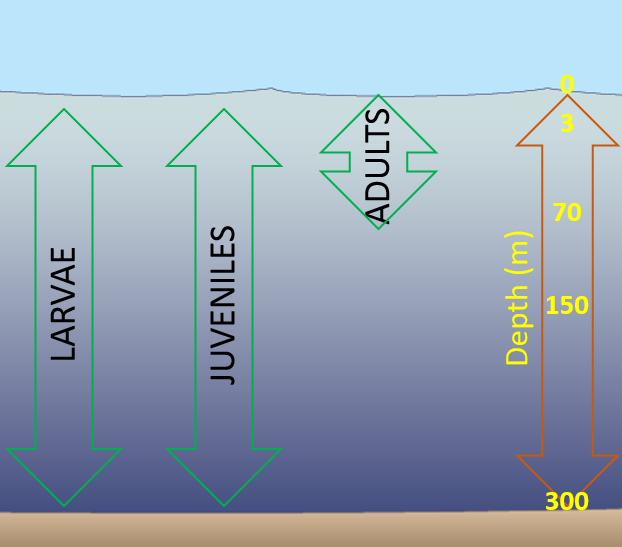
Cobia migrate seasonally, and can be found in the northern Gulf from March to October and in the southern Gulf and south Florida from November to March. In the Gulf, spawning occurs in coastal waters from April to September at temperatures ranging from 23-28 °C (73-82 °F). Cobia which are ready to spawn display a white horizontal stripe down each side of the body. Eggs are found in the top meter (3 ft) of the water column, drifting with the currents, and are estimated to hatch within 36 hours. From May to September, larvae are commonly found in surface waters, and occasionally at depths of up to 300 m (984 ft), where they likely feed on zooplankton. Larvae transition to coastal and offshore waters as juveniles after approximately 25 days, often guided by currents, feeding on small fishes, squid, and shrimp. Adult cobia are found in coastal and offshore waters in depths up to 70 m (230 ft). Adults feed on fishes and crustaceans, including crabs.
Gulf States Marine Fisheries Commission (GSMFC) Management Profile for Gulf of Mexico Cobia
Cobia (Rachycentron canadum) is the only species within the family Rachycentridae and are found throughout most of the tropical and subtropical regions of the world’s oceans. Cobia supports both commercial and recreational fisheries but, in the U.S., recreational landings substantially exceed commercial landings. This species is managed as a federal fishery in the Gulf of Mexico by the Gulf of Mexico and South Atlantic Fishery Management Councils in the Coastal Migratory Pelagic (CMP) Fishery Management Plan. The current stock boundary separating the Atlantic and Gulf Cobia stocks was set between the jurisdictions of the GMFMC and SAFMC which was essentially the Florida Keys.
Download PDF here.
At the March 2017 Annual Spring Meeting of the Gulf States Marine Fisheries Commission, the State-Federal Fisheries Management Committee directed Commission staff to begin development of a Management Profile for Gulf of Mexico Cobia ahead of the anticipated stock assessment which was scheduled to begin in 2019. The Cobia Technical Task Force was established in the fall of 2017 and included representation from each of the state marine resource agencies and others as needed. The management profile was completed in late 2018 and made available in March of 2019 on the Commission’s webpage.


